- Home
- >
- Products
- >
- Bulk Material Conveying Equipment
- >
- Power Plant Pipe Conveyor Belt
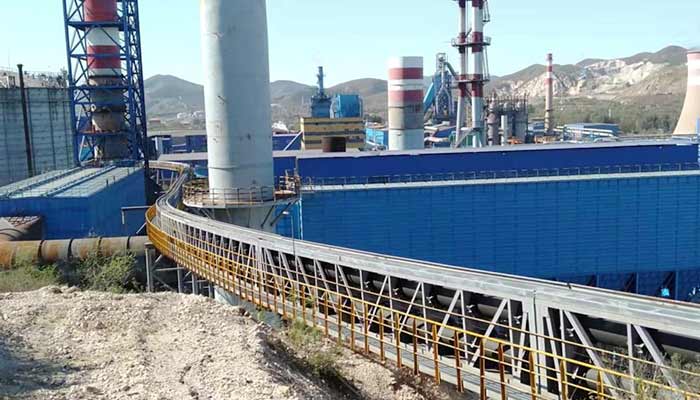
Power Plant Pipe Conveyor Belt
Product origin :China
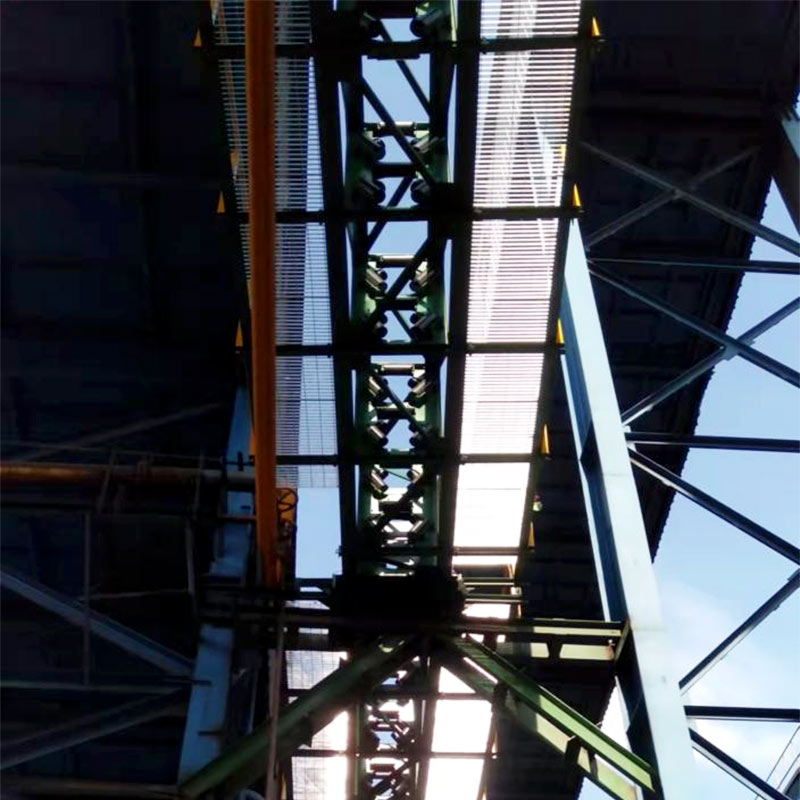
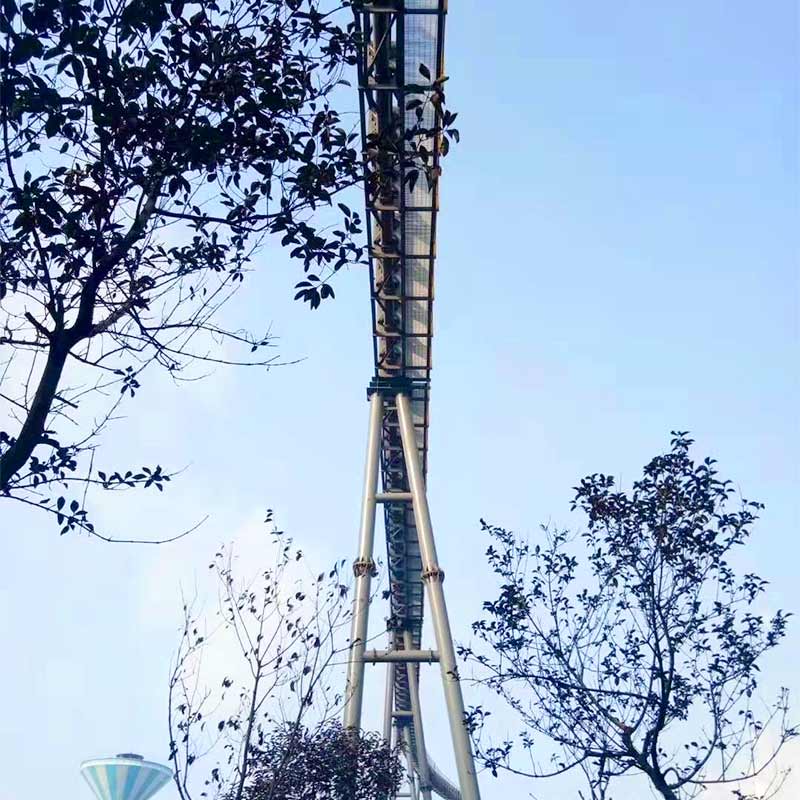
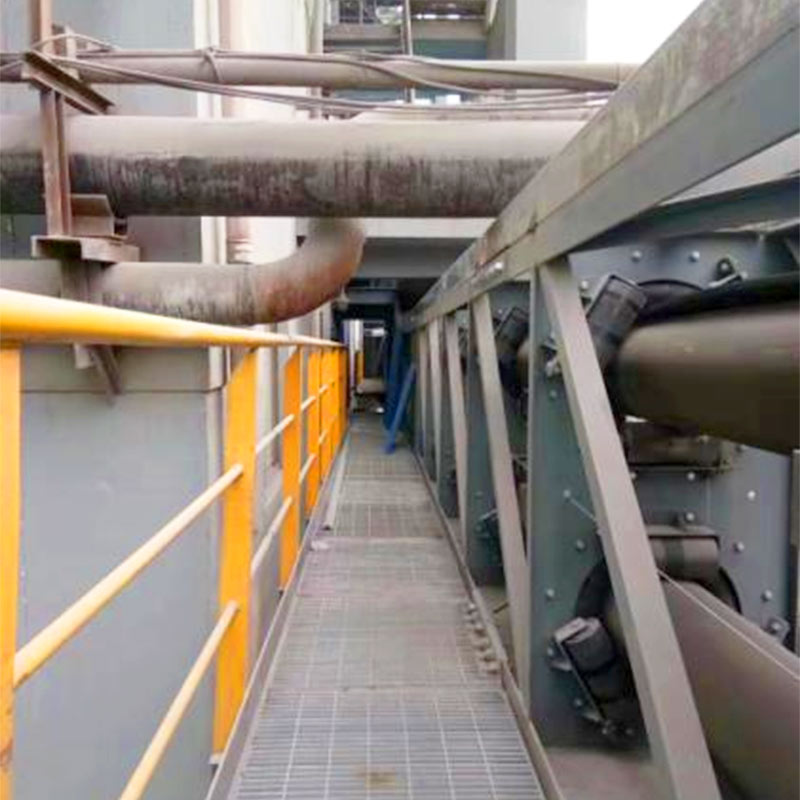
In power generation facilities, the reliable transportation of bulk materials like coal, wood chips, and biomass is critical to ensure uninterrupted energy production. The pipe conveyor belt (also known as tubular belt conveyor) has emerged as an optimal solution, combining environmental protection, high efficiency, and adaptability to complex plant layouts. Designed with a closed cylindrical belt structure, this system addresses the challenges of dust emission, material spillage, and space constraints, making it ideal for power plant applications.
Key Advantages of Pipe Conveyor Belts for Power Plants

1. Enhanced Environmental Protection
● Sealed Transportation: The tubular belt encloses materials completely, reducing dust emissions by up to 99% compared to traditional flat conveyors, meeting strict environmental regulations for power plant operations.
● Weather Resistance: The closed structure protects materials from rain, wind, and dust, preventing fuel degradation and ensuring consistent quality during transport.
2. High Efficiency & Flexible Layout
● Large Capacity: Capable of handling up to 7,200 m³/h of materials (e.g., coal), with adjustable belt speeds (0.8–5.0 m/s) to optimize throughput based on production needs.
● Complex Terrain Adaptability: Can navigate horizontal curves (curvature radius as low as 300× pipe diameter) and vertical inclines, enabling seamless integration into power plant layouts with limited space.
3. Low Maintenance & Durability
● Robust Construction: Made from high-strength rubber or steel cord layers, with all-bolt assembly (no on-site welding) for quick installation and reduced maintenance.
● Long Service Life: Minimal wear from enclosed operation, with components like rollers and tensioning devices designed for 10+ years of continuous use.
Power Plant Pipe Conveyor Belts Technical Parameters: Taking GD200 as an Example
Parameter | Range/Details |
Pipe Diameter | 200 mm (fuel transport) |
Belt Width | 1000 mm |
Conveying Capacity | 66–208 m³/h (66 (0.8 m/s), 83 (1 m/s), 104 (1.25 m/s), 133 (1.6 m/s), 166 (2 m/s), 208 (2.5 m/s)) |
Belt Speed | 0.8–2.5 m/s (variable frequency drive for energy-efficient operation) |
Material Handling | Coal, wood chips, biomass, ash, and other bulk fuels |
Application Scenarios in Power Plants
1. Coal Transportation from Storage to Boiler
Pipe conveyors efficiently move pulverized coal or raw coal from stockyards to boiler feeders, ensuring a steady fuel supply while minimizing dust in the plant.
2. Biomass & Wood Chip Handling
For renewable energy plants, the sealed system prevents debris spillage and maintains the dryness of wood chips, the critical for efficient combustion.
Why Choose Professional Pipe Conveyor Solutions
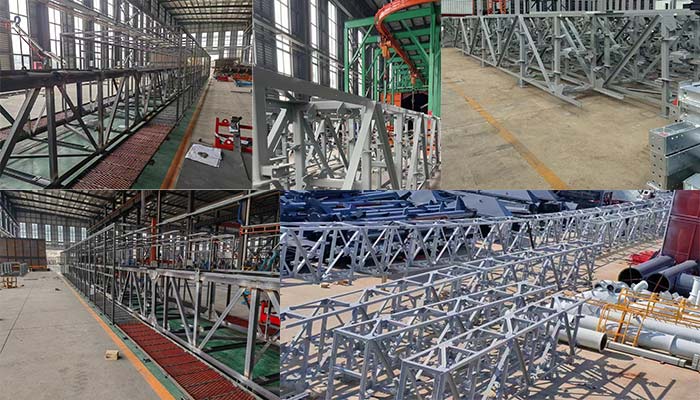

● Custom Design: Engineers use software like Tekla Structures and AutoCAD to tailor layouts for specific plant terrains, reducing installation time by 20–30%.
● Global Service Support: On-site installation guidance, 365-day spare parts supply, and training for operation and maintenance.
● Energy Efficiency: Variable frequency drives and optimized belt speeds reduce power consumption by 15–25% compared to traditional systems.
The pipe conveyor belt is a transformative solution for power plant material handling, combining environmental responsibility, high performance, and operational flexibility. With customizable specifications and robust construction, it ensures uninterrupted fuel supply while minimizing environmental impact. For power plant operators seeking to optimize efficiency and compliance, investing in a professional pipe conveyor system is key to long-term success.
Contact us today for a tailored solution-our team of experts will design a pipe conveyor system that meets your power plant's unique material transport needs.
Customized design of general fabricated steel silo needs to provide: 1. Storage material name 2. Density of storage material 3. Storage material particle size 4. Storage capacity 5. Feeding method 6. Discharge method and size of discharge port 7. The height of the discharge port from the ground...more












